Embedding Operations
Embedding | New Store
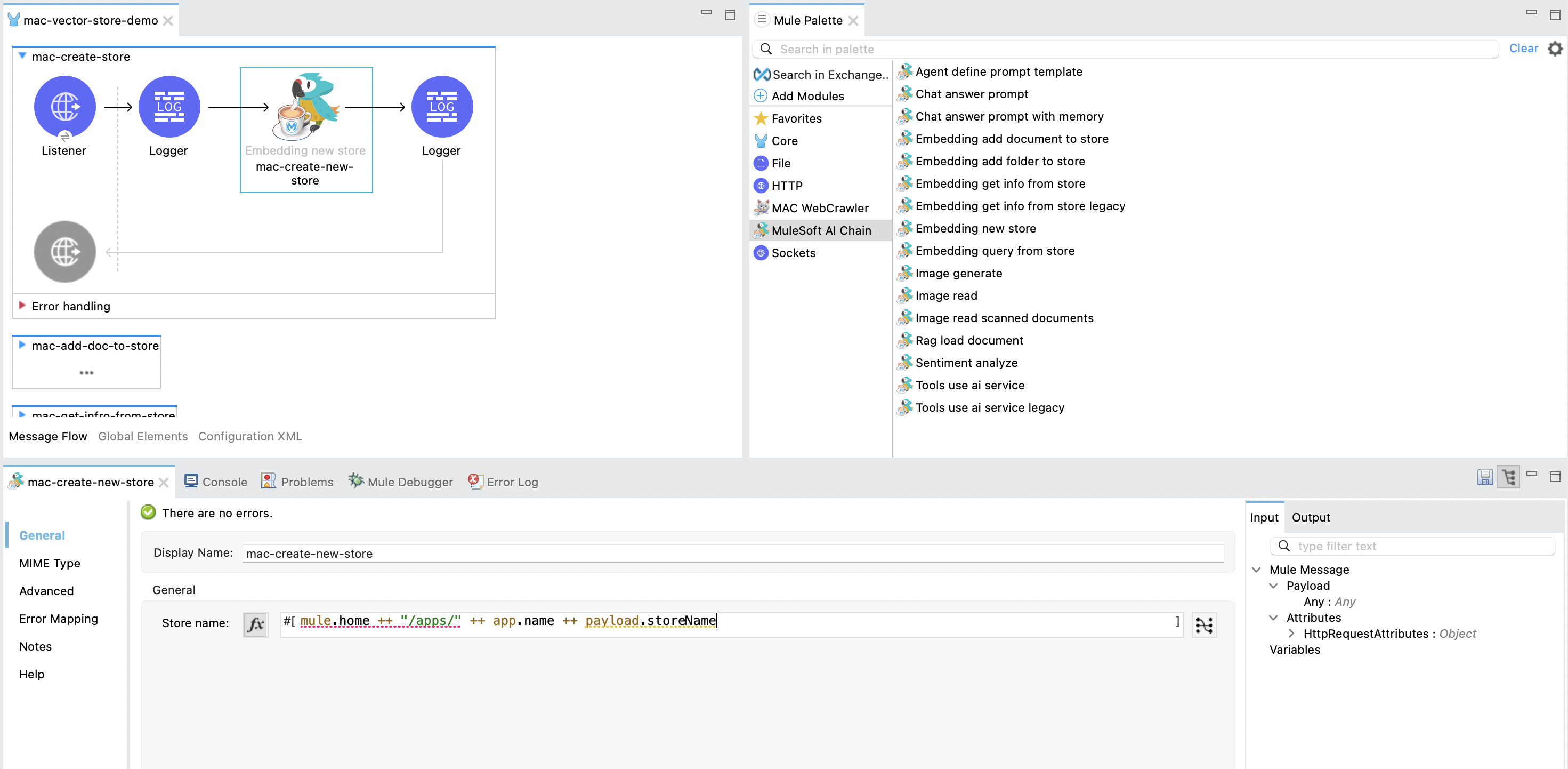
The Embedding new store operation creates a new in-memory embedding and exports it to a physical file. The in-memory embedding in MuleSoft AI Chain persists its data through file exports upon any changes.
Input Configuration
Module Configuration
This refers to the MuleSoft AI Chain LLM Configuration set up in the Getting Started section.
General Operation Fields
- Store Name: Contains the full file path for the embedding store to be saved. If the file already exists, it will be overwritten. Ensure the file path is accessible. You can also use a DataWeave expression for this field, e.g.,
#[mule.home ++ "/apps/" ++ app.name ++ payload.storeName].
XML Configuration
Below is the XML configuration for this operation:
<ms-aichain:embedding-new-store
doc:name="Embedding new store"
doc:id="e3b52f5f-b765-4fad-9ecc-34755f386db4"
storeName='#[mule.home ++ "/apps/" ++ app.name ++ payload.storeName]'
/>Output Configuration
Response Payload
This operation responds with a json payload containing the status of the store. In addition, metadata attributes, such as the store name, are provided separately from the main payload.
Example Response Payload
{
"status": "created"
}Attributes
Along with the JSON payload, the operation also returns attributes, which include information about token usage:
{
"storeName": "knowledge-store"
}- storeName: The name of the generated store.
Example Use Cases
- Create a new in-memory vector store for storing document embeddings.
- Export an in-memory embedding to a physical file for persistence across sessions.
Embedding | Add Document to Store
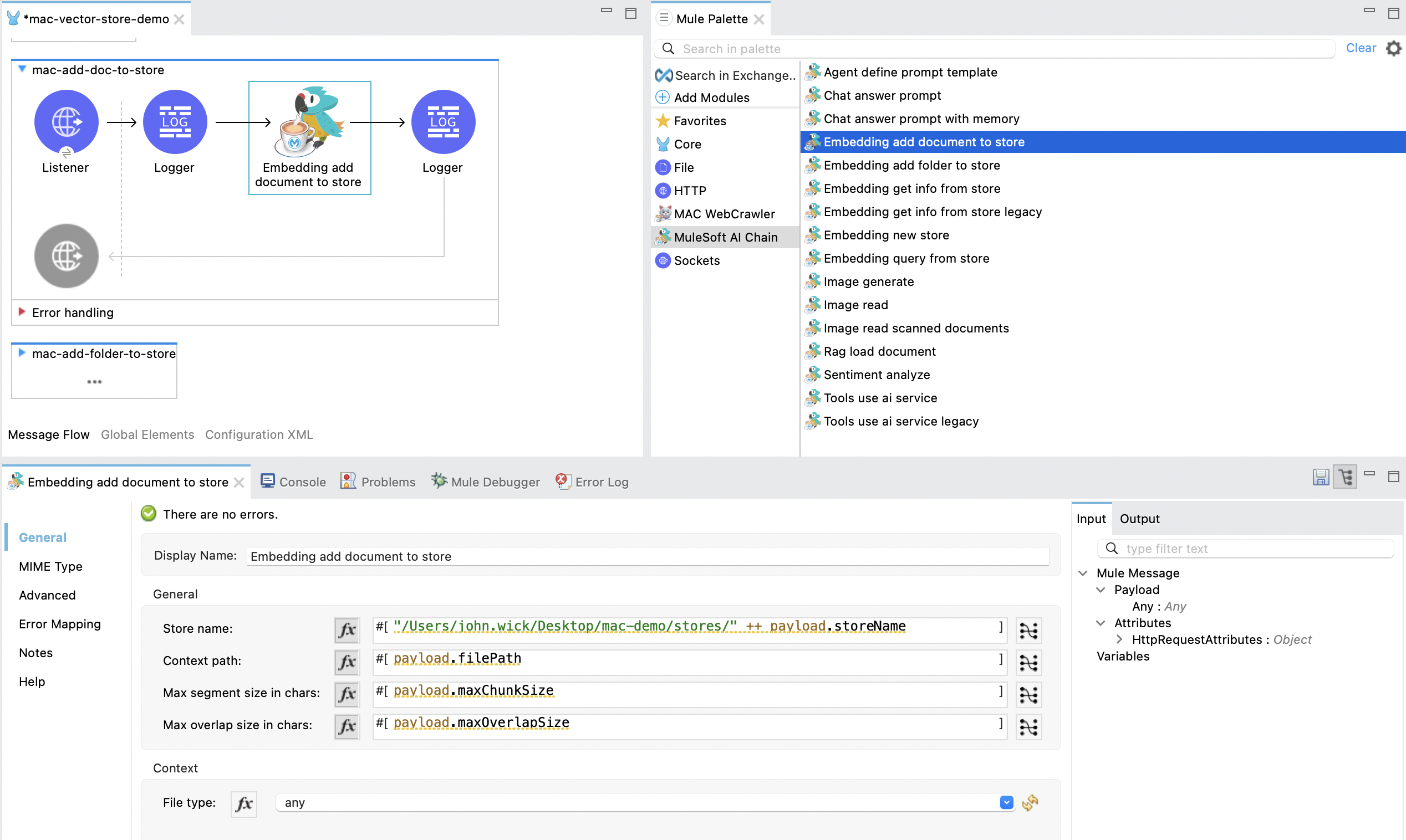
The Embedding add document to store operation adds a document into an embedding store and exports it to a file. The document is ingested into the embedding using in-memory embedding. The in-memory embedding in MuleSoft AI Chain persists its data through file exports upon any changes.
Input Configuration
Module Configuration
This refers to the MuleSoft AI Chain LLM Configuration set up in the Getting Started section.
General Operation Fields
- Store Name: Contains the full file path for the embedding store to be saved. If the file already exists, it will be overwritten. Ensure the file path is accessible.
- Context Path: Contains the full file path for the document to be ingested into the embedding store.
- Max Segment Size: Specifies the maximum size, in tokens or characters, of each segment that the document will be split into before being ingested into the embedding store.
- Max Overlap Size: Defines the number of tokens or characters that will overlap between consecutive segments when splitting the document.
Context Operation Field
- File Type: The type of the document to be ingested into the embedding store. Supported types:
any: Automatically detects the file format and processes it accordingly. This option allows flexibility when the file type is unknown or varied.text: Text files, such as JSON, XML, TXT, CSV, etc.url: A single URL pointing to web content that will be ingested.
XML Configuration
Below is the XML configuration for this operation:
<ms-aichain:embedding-add-document-to-store
doc:name="Embedding add document to store"
doc:id="e8b73dbe-c897-4f77-85d0-aaf59476c408"
storeName='#["/Users/john.wick/Desktop/mac-demo/stores/" ++ payload.storeName]'
contextPath="#[payload.filePath]"
maxSegmentSizeInChars="#[payload.maxChunkSize]"
maxOverlapSizeInChars="#[payload.maxOverlapSize]"
fileType="#[payload.fileType]"
/>Output Configuration
Response Payload
This operation responds with a json payload containing the status of the store. In addition, file-related metadata attributes, such as the file path, store name, and file type, are provided separately from the main payload.
Example Response Payload
{
"status": "updated"
}Attributes
Along with the JSON payload, the operation also returns attributes, which include information about the ingested file:
{
"filePath": "/Users/john.wick/Downloads/mulechain.txt",
"storeName": "/Users/john.wick/Downloads/knowledge-store",
"fileType": "text"
}- filePath: The path of the uploaded file.
- storeName: The name of the store where the document has been added.
- fileType: The type of file ingested.
Example Use Cases
- Add documents (e.g., PDFs, text files) into an embedding store for future retrieval.
Embedding | Add Folder to Store
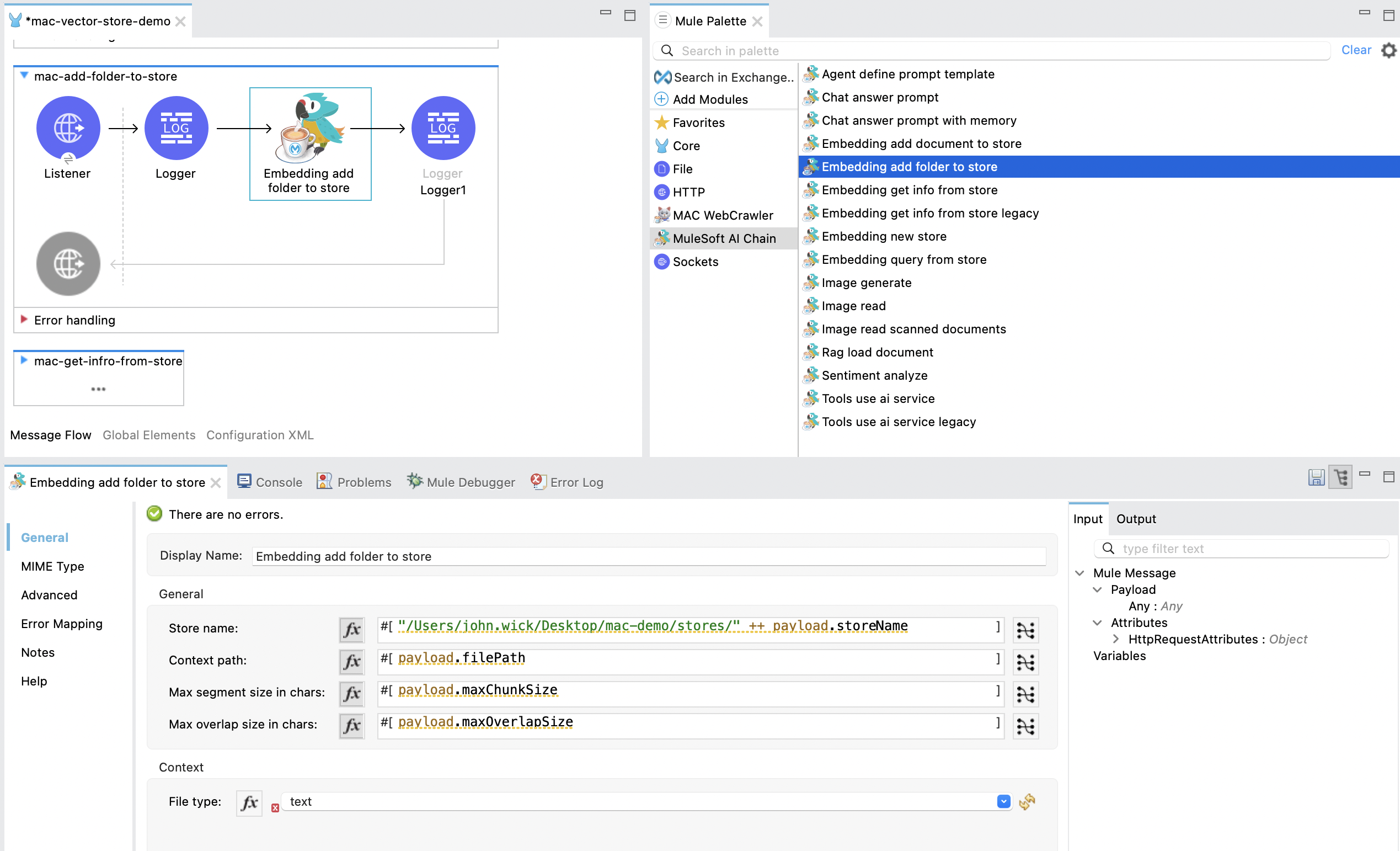
The Embedding add folder to store operation adds a complete folder with subfolder files into an embedding store and exports it to a file. The documents are ingested into the embedding using in-memory embedding. The in-memory embedding in MuleSoft AI Chain persists its data through file exports upon any changes.
Input Configuration
Module Configuration
This refers to the MuleSoft AI Chain LLM Configuration set up in the Getting Started section.
General Operation Fields
- Store Name: Contains the full file path for the embedding store to be saved. If the file already exists, it will be overwritten. Ensure the file path is accessible.
- Context Path: Contains the full folder path to be used for ingesting into the embedding store.
- Max Segment Size: Specifies the maximum size, in tokens or characters, of each segment that the document will be split into before being ingested into the embedding store.
- Max Overlap Size: Defines the number of tokens or characters that will overlap between consecutive segments when splitting the document.
Context Operation Field
- File Type: The type of document to be ingested into the embedding store. Supported types:
any: Automatically detects the file format and processes it accordingly. This option allows flexibility when the file type is unknown or varied.text: Text files, such as JSON, XML, TXT, CSV, etc.url: A single URL pointing to web content that will be ingested.
XML Configuration
Below is the XML configuration for this operation:
<ms-aichain:embedding-add-folder-to-store
doc:name="Embedding add folder to store"
doc:id="231a2afd-8cec-4a70-96c1-3ecef19d02db"
config-ref="MAC_AI_Llm_configuration"
storeName='#[mule.home ++ "/apps/" ++ app.name ++ "/knowledge-center.store"]'
folderPath="#[payload.folderPath]"
/>Output Configuration
Response Payload
This operation returns a json payload containing the status of the store. In addition, folder-related metadata attributes, such as the folder path, file count, and store name, are provided separately from the main payload.
Example Response Payload
{
"status": "updated"
}Attributes
Along with the JSON payload, the operation also returns attributes, which include information about the ingested folder:
{
"folderPath": "/Users/john.wick/Downloads/files",
"filesCount": 3,
"storeName": "/Users/john.wick/Downloads/knowledge-store"
}- folderPath: The absolute path to the folder where the files are located.
- filesCount: The total number of files in the specified folder.
- storeName: The name or path of the knowledge store where the processed document has been stored.
Example Use Cases
- Add a folder of documents (e.g., PDFs, text files) into an embedding store for future retrieval.
- Ingest documents from a specific directory into an in-memory embedding store for contextual analysis.
Embedding | Query from Store
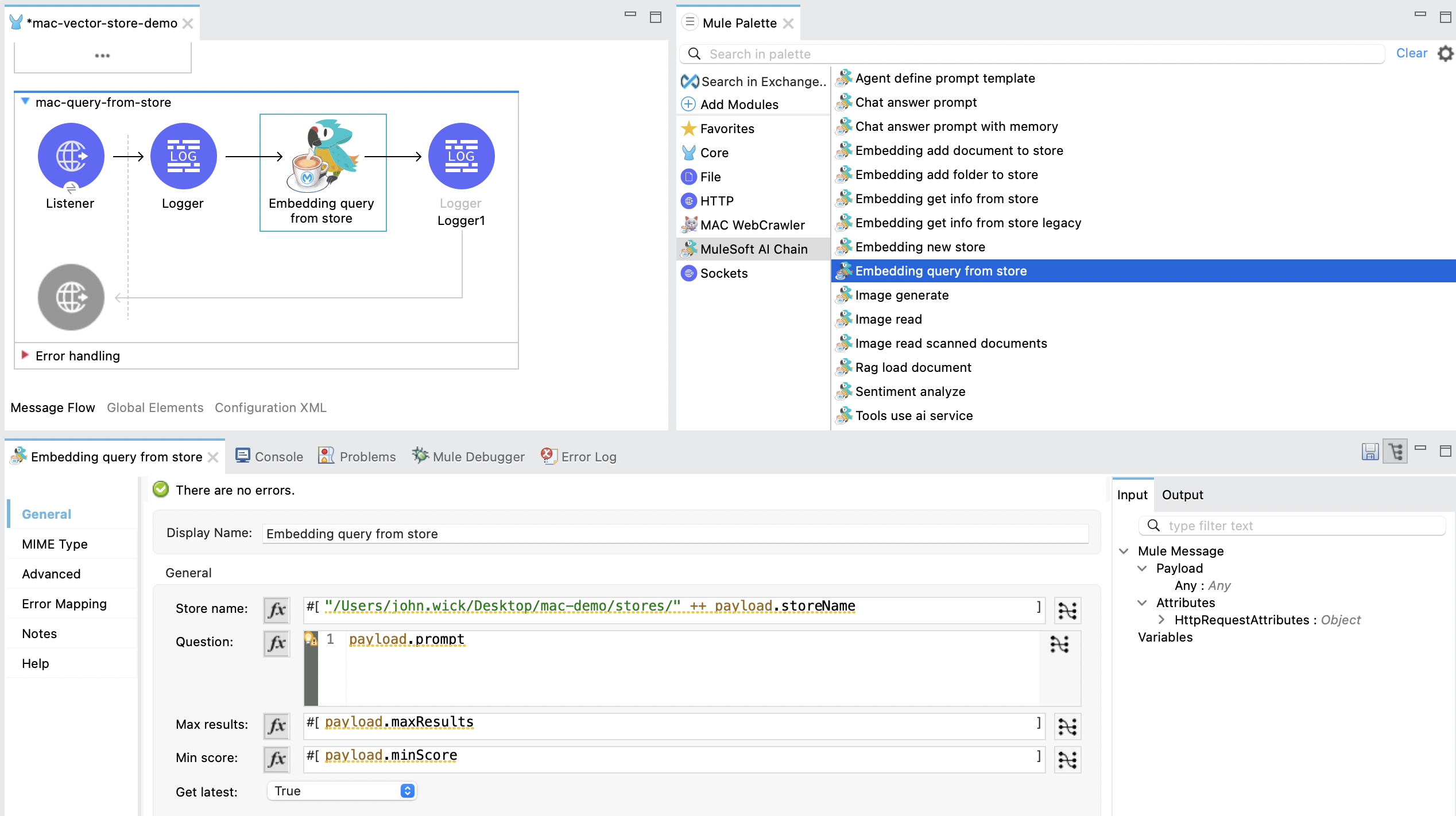
The Embedding query from store operation retrieves information based on a plain text prompt using semantic search from an in-memory embedding store. This operation does not involve the use of a large language model (LLM). Instead, it directly searches the embedding store for relevant text segments based on the prompt. The embedding store is loaded into memory prior to retrieval.
Input Configuration
Module Configuration
This refers to the MuleSoft AI Chain LLM Configuration set up in the Getting Started section.
General Operation Fields
- Store Name: Contains the full file path for the embedding store to be saved. If the file already exists
, it will be overwritten. Ensure the file path is accessible, e.g. #[mule.home ++ "/apps/" ++ app.name ++ payload.storeName].
- Question: The plain text prompt to be sent to the in-memory vector store, which is converted into embedding and used for semantic search to find similar text segments.
- Max Results: Specifies the maximum number of results to be returned with the query.
- Min Score: Defines the minimum score to be used to identify and return results.
- Get Latest: If
true, the store file is loaded each time before running this operation, which might slow down performance. We recommend using this flag only when building the knowledge store. Once deployed with the Mule App, set it tofalsefor better performance.
XML Configuration
Below is the XML configuration for this operation:
<ms-aichain:embedding-query-from-store
doc:name="Embedding query from store"
doc:id="1ee361ea-e62a-4e0f-9c74-0363f8721052"
storeName="#[mule.home ++ "/apps/" ++ app.name ++ payload.storeName]"
question="#[payload.question]"
maxResults="#[payload.maxResults]"
minScore="#[payload.minScore]"
getLatest="true"
/>Output Configuration
Response Payload
This operation returns a json payload containing the main response and a list of relevant sources retrieved from the knowledge store. Each source includes details such as the file path, text segment, and similarity score. Additionally, token usage and query-related metadata are returned separately as attributes.
Example Response Payload
{
"response": "Networking Guide for more information on how to access an application in a specific CloudHub worker.",
"sources": [
{
"absoluteDirectoryPath": "/Users/john.wick/Documents/Downloads/patch 8",
"textSegment": "Networking Guide for more information on how to access an application in a specific CloudHub worker.",
"individualScore": 0.7865373025380039,
"file_name": "docs-runtime-manager__cloudhub_modules_ROOT_pages_cloudhub-fabric.adoc"
},
{
"absoluteDirectoryPath": "/Users/john.wick/Documents/Downloads/patch 8",
"textSegment": "= CloudHub High Availability Features",
"individualScore": 0.7845498154294348,
"file_name": "docs-runtime-manager__cloudhub_modules_ROOT_pages_cloudhub-fabric.adoc"
},
{
"absoluteDirectoryPath": "/Users/john.wick/Documents/Downloads/patch 8",
"textSegment": "[%header,cols=\"2*a\"]|===|VM Queues in On-Premises Applications |VM Queues in Applications deployed to CloudHub",
"individualScore": 0.757268680397361,
"file_name": "docs-runtime-manager__cloudhub_modules_ROOT_pages_cloudhub-fabric.adoc"
}
]
}Attributes
Along with the JSON payload, the operation also returns attributes, which include information about token usage:
{
"minScore": 0.7,
"question": "Who is Amir",
"maxResults": 3,
"storeName": "/Users/john.wick/Downloads/embedding.store"
}- minScore: The minimum similarity score required for a result to be included in the response.
- question: The original query or question submitted by the user.
- maxResults: The maximum number of results that can be returned for the query.
- storeName: The path or name of the knowledge store used to retrieve the data.
Example Use Cases
- Query a vector store for specific information using semantic search.
- Retrieve multiple relevant documents or text segments from an embedding store based on a given prompt.
Embedding | Get Info from Store
The Embedding get info from store operation retrieves information from an in-memory embedding store based on a plain text prompt. This operation utilizes a large language model (LLM) to enhance the response by interpreting the retrieved information and generating a more comprehensive or contextually enriched answer. The embedding store is loaded into memory prior to retrieval, and the LLM processes the results to refine the final response.
Input Configuration
Module Configuration
This refers to the MuleSoft AI Chain LLM Configuration set up in the Getting Started section.
General Operation Fields
- Data: The plain text prompt to be sent to the in-memory vector store, which is converted into embedding and used for semantic search to find similar text segments.
- Store Name: Contains the full file path for the embedding store to be saved. If the file already exists, it will be overwritten. Ensure the file path is accessible, e.g.
#[mule.home ++ "/apps/" ++ app.name ++ payload.storeName]. - Get Latest: If
true, the store file is loaded each time before running this operation, which might slow down performance. We recommend using this flag only when building the knowledge store. Once deployed with the Mule App, set it tofalsefor better performance.
XML Configuration
Below is the XML configuration for this operation:
<ms-aichain:embedding-get-info-from-store
doc:name="Embedding get info from store"
doc:id="913ed660-0b4a-488a-8931-26c599e859b5"
config-ref="MuleSoft_AI_Chain_Config"
storeName='#["/Users/john.wick/Desktop/mac-demo/stores/" ++ payload.storeName]'
getLatest="true">
<ms-aichain:data><![CDATA[#[payload.prompt]]]></ms-aichain:data>
</ms-aichain:embedding-get-info-from-store>Output Configuration
Response Payload
This operation returns a json payload containing the main LLM response, along with a list of relevant sources retrieved from the knowledge store. Each source includes information such as the file path, file name, and a segment of relevant text. Additionally, token usage and query-related metadata are provided separately as attributes.
Example Response Payload
{
"response": "Runtime Manager is a feature within CloudHub that provides scalability, workload distribution, and added reliability to applications.",
"sources": [
{
"absoluteDirectoryPath": "/Users/john.wick/Documents/Downloads/patch 8",
"fileName": "docs-runtime-manager__cloudhub_modules_ROOT_pages_cloudhub-fabric.adoc",
"textSegment": "= CloudHub High Availability Features..."
}
]
}Attributes
Along with the JSON payload, the operation also returns attributes, which include information about token usage:
{
"tokenUsage": {
"outputCount": 89,
"totalCount": 702,
"inputCount": 613
},
"additionalAttributes": {
"getLatest": "true",
"question": "What is MuleChain",
"storeName": "/Users/john.wick/Downloads/knowledge-store"
}
}-
tokenUsage: Provides information on the token usage for the operation:
- outputCount: The number of tokens generated in the response.
- totalCount: The total number of tokens processed for the entire operation, including input and output.
- inputCount: The number of tokens processed from the input query or document.
-
additionalAttributes: Includes metadata related to the query and store:
- getLatest: Indicates whether the knowledge store is reloaded for each operation (true/false).
- question: The original query or question submitted by the user.
- storeName: The path or name of the knowledge store used in the operation.
Example Use Cases
- Query a knowledge store with a plain text prompt and receive a refined response powered by an LLM.
- Retrieve and interpret data from documents in an embedding store, with enhanced context from the LLM.